A shaper machine can be found in many mechanical workshops and manufacturing businesses. It plays a crucial role in producing numerous parts, tasks, and other items.
So, let us discuss what a shaper machine is, and how it functions along with its advantages/disadvantages and applications.
Table of Contents
What is A Shaper Machine?
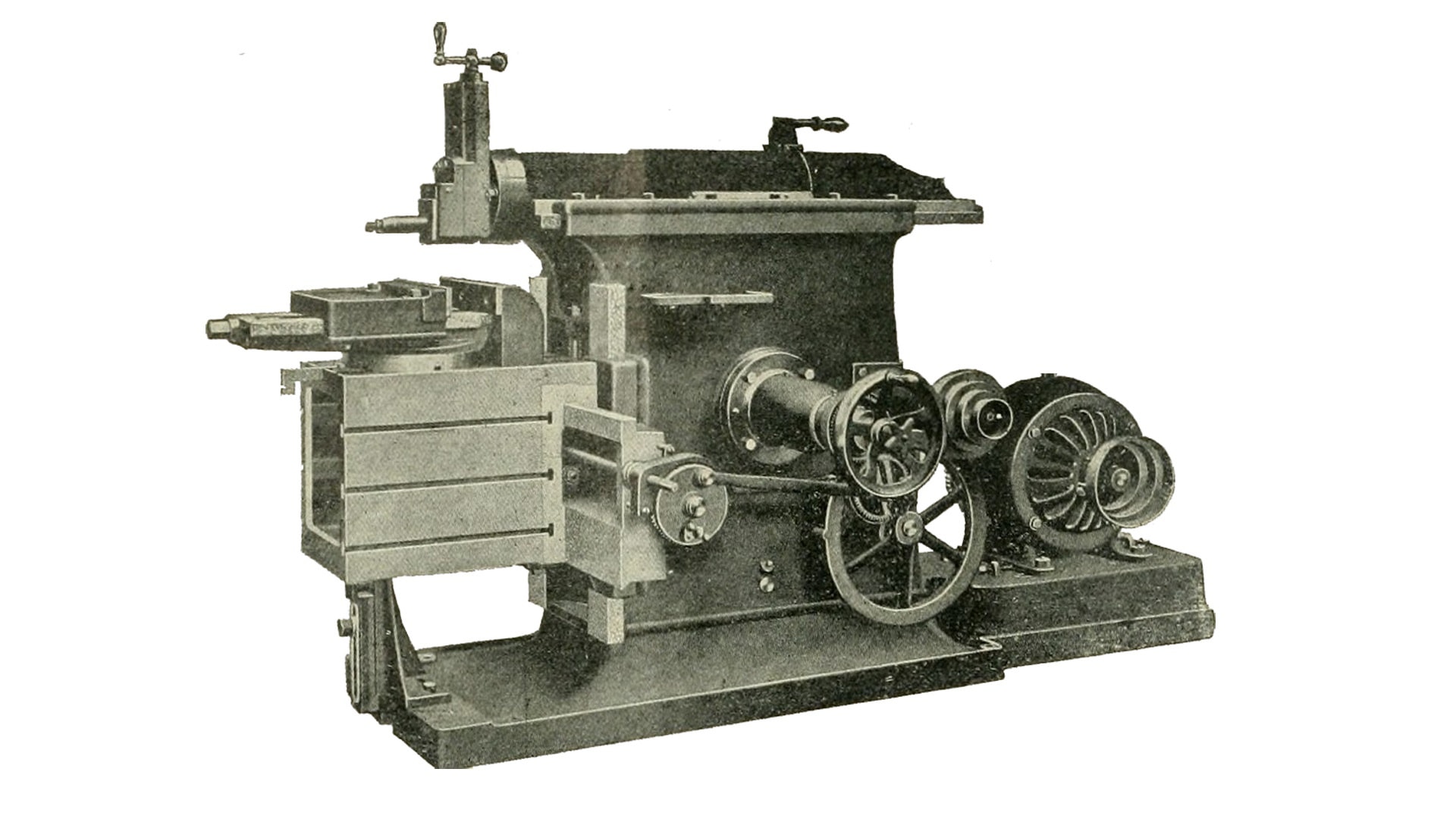
A Shaper Machine is a type of machine that is primarily used to make vertical, horizontal, or inclined flat surfaces. Like tools used in lathe operations, it uses straight-line reciprocating single-point cutting tools.
The workpiece is clamped in the machine vice, and the tool reciprocates on it with the help of a ram. This machine moves in a straight line and cuts along a straight tool path. The machine’s cut is comparable to that of a lathe machine.
The helical cut is made by the lathe machine, whereas the linear cut is made by the shaper machine.
Working Principle of A Shaper Machine
The principle behind a shaper machine is simple yet complex. The workpiece is mounted over the table, and the single-point cutting tool is held in the ram by a shaper machine.
The ram that holds the tool reciprocates over the workpiece, cutting metal on the forward stroke and leaving no metal on the return stroke, which is known as an idle stroke. At the end of each cutting stroke, the feed is delivered.
The cutting stroke is usually performed at a medium pace. In contrast, an idle stroke is performed at a rapid speed, thanks to the quick return mechanism.
Quick Return Motion Mechanism is the mechanism that works in the shaper machine. The principle involved in this mechanism helps it to become an efficient machine.
The Slider moves quickly in the forward stroke, removing material from the workpiece. The Slider moves quicker in the return stroke than the forward stroke, which means it takes less time to return, which is why it’s called a return stroke.
The quick return mechanism provided the motion to the cutting tool, which was used to achieve cutting depth. The pawl and ratchet mechanism controls the feeding motion.
Parts of Shaper Machine
The shaper machine is made up of five basic components:
1) Base
It is the most crucial component of the shaper. Other machining tools are supported by the base. The base is composed of cast iron and is hollow. This hollow form reduces the vibration that may otherwise be caused. The base’s design is intended to support the machine’s weight.
2) Column
It is made of cast iron and is installed on the base. On the column, on which the ram reciprocates, there are two guideways. The reciprocating ram and worktable are supported by the column.
3) Table
The table can be swiveled in any direction. To handle heavy applications, the table is clamped to become rigid. It is a critical component of the shaper machine. On both the top and bottom sides, T-type bolts are used for clamping.
4) Ram
There are two guideways on the column of the machine. With a single-point cutting tool, Ram reciprocates and carries the tool’s head. Because of the tool head in the clapper box, the cutting action occurs on the forward stroke of the ram. The down feed screw determines the depth of the cut.
5) Cross-rail
It’s attached to the table’s surface, where the saddle is. The table can move vertically, thanks to the elevating screw and cross-rail. The table is moved horizontally by moving the saddle with the cross-feed screw.
6) Saddle
The saddle is attached to the cross-rail to keep the table in place. By spinning the cross-feed screw, the movement of the saddle forces the table to move crosswise.
7) Tool Head
With the help of a down-feed screw handle, the tool head secures the cutting tool and allows it to move vertically and angularly. During the return stroke, the tool’s head enables automated relief.
The vertical side of the tool head is made up of a swivel base with graduated degrees. As a result, the vertical slide can be positioned at any angle with respect to the work surface.
Specifications of A Shaper Machine
The factors that influence the specifications of a shaper machine include:
- The maximum length of the stroke ram.
- Different types of drives (Crank, Gear, and Hydraulic type)
- The power supply of the machine
- To set up the machine, you’ll need some floor space.
- The weight of the machine is in tonnes.
- Cutting Feed-to-Return Stroke Ratio
- The angular movement of the table.
Operations Performed on A Shaper Machine
In a shaper machine, there are four different sorts of operations:
– Cutting horizontally
The work installed on the machine table is moved in a cross direction with regard to the ram movement to the machine’s horizontal surfaces. The clapper box can be angled vertically or slightly towards the uncut surface.
During the return stroke, the tool lifts automatically, thanks to this design. At the same time, the tool doesn’t drag on the machined surface.
– Cutting vertically
A vertical cut is done while cutting the edges of workpieces, or squaring up a block, or machining a shoulder.
The feed is provided to the tool by moving the vertical slide’s down feed screw. For this reason, the table cannot be moved vertically. The apron is swiveled away from the machined vertical surface.
– Slanted cutting
Any angle other than a straight angle to the horizontal or vertical plane is considered an angular cut. The work is placed on the table, and the vertical slide of the tool head is swiveled from its vertical position to the necessary angle, either to the left or to the right.
– Irregular cutting
This procedure is performed with a round-nose instrument. The apron can be placed vertically for a shallow cut, but if the curve is fairly acute, the apron should be swiveled to the right or left away from the surface to be cut.
Applications of A Shaper Machine
A Shaper Machine has diverse applications. It is used to machine flat and straight surfaces along with being used in internal splines and gear teeth. Gear tooth cutting can be done for the blind holes. Dovetail sliders are made with this material.
This is an excellent tool for obtaining the smoothness of a rough surface. It is also utilized for milling with an electric discharge.
Milling or other machining operations are unable to create holes with tight corners in an uneven shape. These kinds of holes can be made by the machine.
Different Types of Shaper Machines
Shaper machines are classified by the sort of drive mechanism they use.
– Crank type
The forward stroke is produced by a half rotation of the crank, and the return stroke is produced by another half revolution of the crank. The forward and return strokes must have various speeds to meet the requirements of a shaper machine.
Whitworth’s quick return mechanism, which is one of the inversions of a single slider-crank mechanism, is utilized between the Ram and the crank to get the varied velocity of Ram even while the crank is revolving at uniform velocity.
– Ratchet and Pawl Mechanism
The workpiece will only get an intermittent feed of the automated feed required for shaping operations. In the shaping operation, the ratchet and pawl mechanism will be used to obtain the intermittent feed.
– Rocker Arm Clapper Box
To accomplish different shaping operations, a clapper box can be used in conjunction with the Rocker ARM to reduce tool wear.
Advantages of Shaper Machine
Let’s look at the advantages of using Shape Machine:
- The shaper machine has the benefit of cheap tooling costs. In the shaper machine, a single-point cutting tool is employed, which is affordable and readily available. Machining can be done more efficiently and at a lower cost with a single-point cutting tool.
- In machining, the cutting stroke has a defined stopping point, which is useful.
- This machine has the advantage of being simple to operate. An operator can readily operate the machine with only a little knowledge of the machine. The machine requires some abilities to use, but an experienced person can operate it flawlessly.
- The quick return technique can be used on both flat and angled surfaces.
- Machining is a simple process that can be completed without difficulty.
Disadvantages of Shaper Machine
So, where does a Shaper Machine lack applicability? Let’s see a few points as its disadvantages. They are listed below:
- The machining on this machine took longer. Machining has to cut and return strokes, and it takes longer than milling machines and other equipment.
- For cutting, there is only one tool available. The workpiece cannot be sliced in both directions.
- The shaper machine has a slow cutting speed.
- It can only change the shape of one workpiece at a time.
- This only applies to workpieces (stock) with a length of greater than 25cm.
Final Words
So, here we went through the detailed guide of the Shaper Machine. We discussed its definition, parts, workings, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and specifications.
The machine uses a quick return mechanism for shaping different workpieces horizontally, vertically, and angularly. Though it is simple, affordable, and readily available, it cannot slice the workpiece in both directions.
It finds its applications in milling, gear tooth cutting, and smoothing the workpiece.
Next, you should also read the articles whose links are provided below: